Voice Controlled Lights using Raspberry Pi
Voice controlled
home application
Today we are building a very useful
project in which we can control the LED lights using our voice through Smart
Phone. In this project, we will send voice commands from Smart Phone to
Raspberry Pi using Bluetooth Module and Raspberry Pi will receive that
transmitted signal wirelessly and will perform respective task over the
hardware. We can replace the LEDs with the AC home appliances using relays and
can build a Voice Controlled Home Automation Project.
Components Used:
- · Raspberry Pi 3 (any model shall work)
- · Bluetooth Module HC-06
- · Bread board
- · 100 ohm Resistors (3)
- · LED’s (blue, red, green)
- · Connecting wire
- · Power Supply
- · Ethernet cable
- · Android Phone
Bluetooth Module:
Bluetooth module consists two things
one is Bluetooth serial interface module and a Bluetooth adaptor. Bluetooth
serial module is used for converting serial port to Bluetooth.
Bluetooth Module HC06 and Raspberry Pi 3
How to operate Bluetooth module:
You can directly use the Bluetooth
module after purchasing from market, because there is no need to change any
setting of Bluetooth module. Default baud rate of new Bluetooth module is 9600
bps. You just need to connect rx and tx to controller or serial converter and
give 5 volt dc regulated power supply to module.
Bluetooth module has two modes one is
master mode and second one is slave mode. User can set either mode by using
some AT commands. Even user can set module’s setting by using AT command. Here
is some commands uses are given:
First of all user need to enter AT
mode with 38400 bps baud rate by pressing EN button at Bluetooth module or by
giving HIGH level at EN pin. Note: all commands should ends with \r\n (0x0d and
0x0a) or ENTER KEY from keyboard.
After it if you send AT to module then
module will respond with OK
AT à Test Command
AT+ROLE=0 à Slave Mode select
AT+ROLE=1 à Master Mode select
AT+NAME=xyz à Set Bluetooth
Name
AT+PSWD=xyz à Set Password
AT+UART=<value1>,<value2>,<value3> à set Baud rate
Eg.
AT+UART=9600,0,0
Pin Description of HC-06 Bluetooth
Module:
1. STATE à Open
2. Rx à Serial receiving pin
3. Tx à Serial transmitting pin
4. GND à ground
5. Vcc à +5volt dc
6. KEY à to enter in AT mode
Working Explanation:
Working of this Voice Controlled LEDs
project is very easy. In this project we have used three LEDs of different
colors (Blue, Red and Green). A HC-06 Bluetooth Module is used for receiving
voice commands output in string format. Raspberry Pi receives that incoming
string from Bluetooth Module and compares with predefined string and performs
respective task.
In this project, to provide the voice
commands to Raspberry Pi from our Smart Phone, we have used AMR Voice App in
Android Phone (Android Meets Robots : Voice Recognition).
AMR Voice App installation and
configuration:
AMR Voice App can be downloaded and
installed from the Google Play Store. You also need to install Google Voice App
for this project. AMR Voice app takes the voice as input and converts it into
text string using Android mobiles internal voice recognition (Google Voice App)
and sends this converted text serially over Bluetooth.
Now open the AMR voice app, go in
option menu and connect it to Bluetooth module by clicking over ‘Connect
Robot’:
Now user can tap over the Mic symbol
on mobile screen and speak predefined Voice commands to operate the LEDs:
1. “blue light
on” (only blue LED turned on)
2. “blue light
off” (only blue LED turned off)
3. “red light
on” (only red LED turned on)
4. “red light
off” (only red LED turned off)
5. “green light
on” (only green LED turned on)
6. “green light
off” (only green LED turned off)
7. “all lights
on” (blue, red and green LEDs turned
on)
8. “all lights
off” (blue, red and green LEDs turned
off)
9. “blink” (all LEDs start blinking with a
100 millisecond time period)
Then AMR voice app records this voice
and sends it to Google Voice app to convert it into the text string format. Now
this converted string is sent to Raspberry Pi via Bluetooth module and
Raspberry Pi reads this string from UART port and store in a string in the
code. And then compare it with predefined strings, if any match occurs then
Raspberry Pi takes a respective action or performs a task.
Circuit Explanation:
Circuit of this project is very
simple, which contains Raspberry Pi 3 Board, LEDs and Bluetooth Module (HC-06).
Raspberry Pi reads the Bluetooth Module and control the LEDs accordingly. LEDs
Blue, Red and Green are connected at GPIO 17, 27 and 22. Rx and Tx of Bluetooth
Module are directly connected to Tx and Rx pins of Raspberry Pi. Remaining conn
ections are shown in circuit diagram.
Raspberry Pi Configuration and Python
Program:
We are using Python language here for
the Program. Before coding, user needs to configure Raspberry Pi. You can check
our previous tutorials for Getting Started with Raspberry Pi and Installing
& Configuring Raspbian Jessie OS in Pi.
After that you need to run following
commands to run latest updates on Raspbian Jessie:
sudo apt-get
update
sudo apt-get
upgrade
After it we need to install Raspberry
Pi GPIO development tool, it can be installed by following commands:
sudo apt-get
install python-dev
sudo apt-get install
python-rpi.gpio
Then user needs to configure serial
port of Raspberry Pi. Here we have used Raspberry Pi 3 for this project. So
user needs to configure serial port according to their Raspberry Pi version.
For Raspberry Pi 3, first user needs to disable console login via serial port,
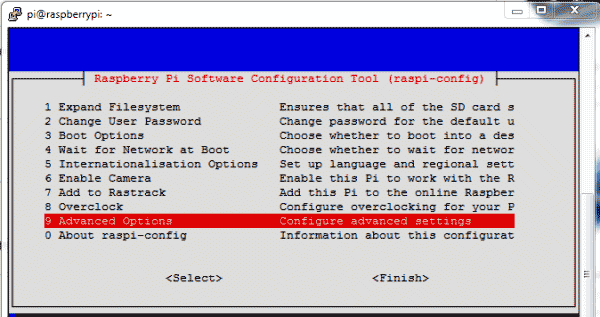
through RPi Software Configuration Tool. Open it by using below command:
sudo raspi-config
Then go to ‘Advance Options’, select
‘Serial’ and ‘Disable’ it.
After this we need to disable inbuilt
Bluetooth of Raspberry Pi 3 by adding dtoverlay=pi3-miniuart-bt at the end
of /boot/config.txt file:
sudo nano
/boot/config.txt
After adding the line reboot RaspberryPi by issuing sudo reboot command.
Finally login in Raspberry Pi again
and configure /boot/comline.txt file:
sudo nano
/boot/comline.txt
And edit the file as below:
dwc_otg.lpm_enable=0
console=tty1 console=serial0,115200 root=/dev/mmcblk0p2 rootfstype=ext4
elevator=deadline fsck.repair=yes rootwait
Now you can run the Python program
given below in Raspberry Pi and you are done! Program is easy and can be easily
understandable.
So here we have completed building our
Voice Controlled Devices using Raspberry Pi. You can further enhance it and
modify it for controlling AC home appliances by adding relays.
Code:
import serial
import RPi.GPIO
as GPIO
import os, time
led1=17
led2=27
led3=22
GPIO.setwarnings(False)
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
GPIO.setup(led1,
GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(led2,
GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(led3,
GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.output(led1
, 0)
GPIO.output(led2
, 0)
GPIO.output(led3
, 0)
Serial =
serial.Serial("/dev/ttyS0", baudrate=9600, timeout=2)
data1=""
data=''
while 1:
while data != '#':
data = Serial.read(1)
data1+=data
print data1
if data1.find("blue light
on")>0:
GPIO.output(led1 , 1)
print "Blue Light on"
if data1.find("blue light
off")>0:
GPIO.output(led1 , 0)
print "Blue Light Off"
if data1.find("red light on")>0:
GPIO.output(led2 , 1)
print "Red Light on"
if data1.find("red light
off")>0:
GPIO.output(led2 , 0)
print "red Light Off"
if data1.find("green light
on")>0:
GPIO.output(led3 , 1)
print "Green Light on"
if data1.find("green light
off")>0:
GPIO.output(led3 , 0)
print "Green Light Off"
if data1.find("all lights
on")>0:
GPIO.output(led1 , 1)
GPIO.output(led2 , 1)
GPIO.output(led3 , 1)
print "All Lights on"
if data1.find("all lights
off")>0:
GPIO.output(led1 , 0)
GPIO.output(led2 , 0)
GPIO.output(led3 , 0)
print "All Light Off"
if data1.find("blink")>0:
for k in range (100):
GPIO.output(led1 , 1)
GPIO.output(led2 , 1)
GPIO.output(led3 , 1)
time.sleep(0.1)
GPIO.output(led1 , 0)
GPIO.output(led2 , 0)
GPIO.output(led3 , 0)
time.sleep(0.1)
Serial.flush();
data="";
data1="";
So guys do those works practically and enjoy. For any help contact us on facebook:













Comments
Post a Comment